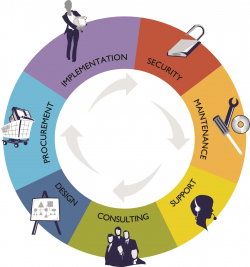
The Cyclical Nature of Technology
|
Information Technology Understood as Cycles |
|
|
Secure |
There are multiple aspects of security including hardware, software and physical. The most important aspect of security is access. The most secure IT Infrastructure is an unusable infrastructure. Establishing a good balance between usability and security is a regular activity across the multiple platforms managed. |
|
Maintain |
Maintenance involves the activities that keep hardware, and software in top condition and assuring that it is running error free and maximizing up-time. One of the most important aspects of maintenance is monitoring of critical hardware and applications. |
|
Support |
The users in any organization require assistance when technology is broken or are interested in enhancing existing technology. User support is a corner stone in an Information Technology department, frequently the gateway into improved performance and efficiency. |
|
Consult |
When change is needed, whether it is municipal services expansion or contraction, a plan is required. Consulting is the process of understanding the required change and properly documenting it and evaluating options for future implementation activities. |
|
Design |
After the documentation and discovery is completed the delivery of a comprehensive design is used to engage stakeholders. The consult and design processes operate as a mini-cycle enabling the refinement of the end change and metrics for success. |
|
Procure |
A completed design leads to the approval and expenditure of financial resources. Financial resources are converted to hardware, software and labor. |
|
Implement |
Hardware and software are deployed in a manner that is both expeditious and guaranteed to operate within the established design. |
The Completion of the Implementation cycle is not the end, the Information Technology department must continue to secure, maintain, and support the implemented change.